Through divergent evolution organisms may develop homologous structures. Alfred Russel Wallace is regarded as the father of biogeography.

7 Animals We Used To Think Were Extinct But Aren T Extinct Animals Animals Science Nature
Noting that human babies are born helpless Anaximander speculated that humans must have descended from some other type of creature whose young could survive without any.

Geographic variation definition evolution. Geographical variation refers to differences among populations in genetically based traits across the natural geographic range of a species. Any variation of a species which is dependent on climate or other geographical conditions. A function of geographic variation in the characteristics of regularity in availability of and optimality in level of certain resources-especially water-vital to all life forms.
Evolution theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants animals and other living things on Earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations. For an event to be considered an instance of evolution changes have to occur on the genetic level of a population and be passed on from one generation to the next. Geographic variation in allozymes in a ring species the plethodontid salamander Ensatina eschscholtzii of western North America.
The relative importance of directional change random walks and stasis in the evolution of fossil lineages. 3 Moritz C CJ. Biological evolution is defined as any genetic change in a population that is inherited over several generations.
There is no precise scientific definition for this term but it is often used to refer to the emergence or modification of taxa at or above the genus level. The adaptive significance of intraspecific trends of variation in wing length and body size among bird species. Genetic variation is the presence of differences in sequences of genes between individual organisms of a species.
Evolutionary principles of geographic variation began to emerge early as the field of evolutionary biology developed within the biological sciences. Understanding the factors that give rise to and maintain geographical variation helps elucidate the causes and consequences of evolution. Studies of animal behavior often assume that all members of a species exhibit the same behavior.
These are anatomically similar structures. It enables natural selection one of the primary forces driving the evolution of life. The theory of evolution is one of the fundamental keystones of modern biological theory.
Geographic Variation in Behavior shows that on the contrary there is substantional variation within species across a wide range of taxa. Geographic size variation in birds and its relationship to climate. A geographic mosaic of coevolution GMC occurs when local variation in species interactions produces a spatially variable pattern of reciprocal adaptation in these species.
Biogeography provides evidence of evolution. Geographic variation definition is - the differentiation of distinctive subdivisions from geographically isolated parts of a potentially interbreeding population due to restriction of interbreeding between fractions and natural selection of locally valuable mutations. These changes may be small or large noticeable or not so noticeable.
Allopatric speciation and peripatric speciation occur when the reproductive barrier is caused by a physical or geographical barrier such as a river or mountain range. In the simplest case we divide these factors into purely genetic versus environmental components to tease. A biogeographer is a person who studies the geographic distribution of plants and animals on the earth.
Ideas aimed at explaining how organisms change or evolve over time date back to Anaximander of Miletus a Greek philosopher who lived in the 500s BCE. Describes several possible mechanisms for gradual change and argues that knowledge of geographic variation is critical for pattern interpretation. The study of biogeography became popular due to the work of Alfred Russel Wallace an England exploraer 1823-1913.
A more precise definition of Bergmanns Rule. Theory of Evolution. The critical concept is that populations should probabilistically tend to extend toward areas where conditions are more.
Evolutionary relationships within the Ensatina eschscholtzii complex confirm the ring species interpretation. Since the process is gradual there is no particular point at which it is possible to say that the two populations have become two different species. Two geographically separate populations that at one time were members of the same species later may have diverged into two different species.
Geographic variation of species sometimes featuring distinct subspecies and often having characteristic traits is determined by geographic variables such as climate or ecological niche as well as population genetic factors. Alternatively sympatric speciation and parapatric speciation take place within the same geographical area.

Evolution Assessment Packet Two Quizzes Two Tests Teaching Critical Thinking Middle School Science Resources Critical Thinking Activities
Https Courses Botany Wisc Edu Botany 422 Lecture Pdf Geovariatspec Pdf

Evolution Concept Map Evolution Concept Map Concept Map Biology Lessons

The Tree Of Life National Geographic Society

Speciation Definition Causes Process Types Examples

Brain Definition Parts Functions Facts In 2021 Brain Size Human Evolution Evolution Activities
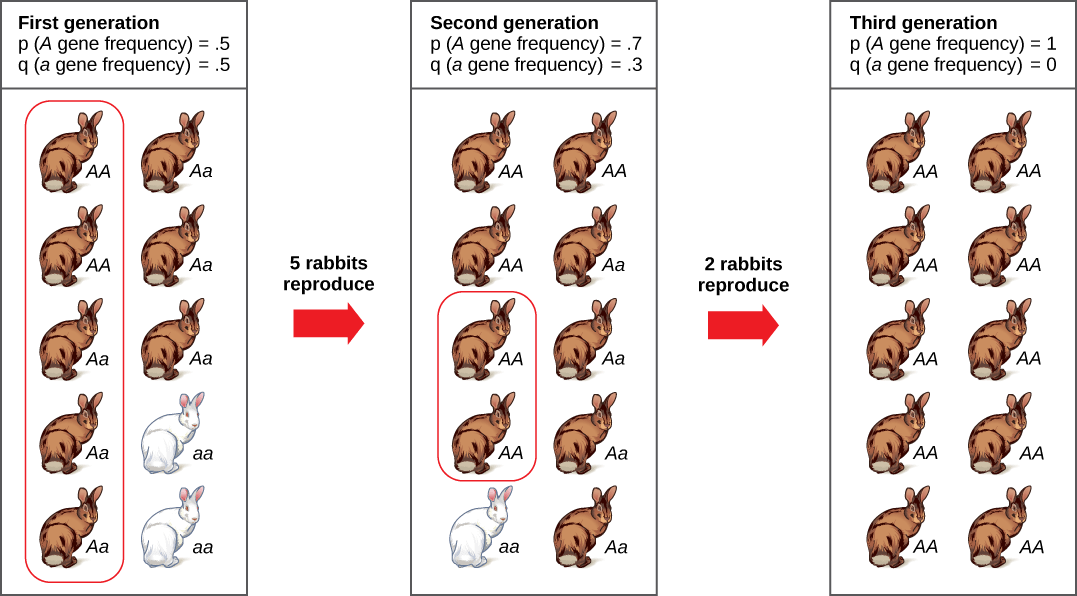
Other Mechanisms Of Evolution Biological Principles

Possibly Helpful Image Evolution Genetic Variation Homework Help
0 Response to "22+ Geographic Variation Definition Evolution"
Post a Comment